Memory Consistency and Cache Coherence
objdump file
1 | Disassembly of section .plt: |
.plt节主要实现了使用过程链接表(Procedure Linkage Table)实现延迟绑定的功能。
openmp相关的执行
omp_outlined函数
问题:objdump 程序 有许多 类似 <.omp_outlined..16>: 的函数,但是main函数里并没有调用。实际openmp是怎么执行这些代码的呢?
在使用了OpenMP指令的C/C++程序编译后,编译器会自动生成一些名为.omp_outlined.的函数。这些函数是OpenMP所需要的运行时支持函数,不是直接在main函数中调用的,其执行方式主要有以下几种:
- 一些关键的运行时函数,如线程创建、同步等,是在程序启动时由OpenMP运行时库初始化和直接调用的。
- 对于并行region,编译器会在主线程发起并行时调用对应的
.omp_outlined.函数创建线程并发布工作。 - 一些工作分配,同步等调用也是隐式通过运行时库的支持函数实现的。
- 对于并行循环,编译器会将循环体移动到
.omp_outlined.函数,在循环分配工作时调用。 - 减少指令,作用域变化等也会引发这些函数的调用。
所以.omp_outlined.函数的执行是隐式通过运行时库触发和调度的,不需要用户代码直接调用。它们是OpenMP实现所必须的,由编译器和运行时库协调完成。用户只需要编写OpenMP指令,不必关心具体的调用细节。
总体来说,这是一种让并行执行透明化的实现机制,减少了用户的工作量。
OpenMP的汇编代码
不同平台不同,有GOMP_parallel_start开头的。也有如下x86平台的
1 | 405854: 48 c7 84 24 a0 00 00 movq $0x4293b9,0xa0(%rsp) |
这段汇编代码实现了OpenMP中的并行构造,主要执行了以下几个步骤:
- 在栈上写入一个常量0x4293b9,可能是team的参数 (48 c7 84 24)
- 准备参数,获取rsp+0x90地址到rdi作为第1参数 (%rdi)
- 设置edx为0x405f10,可能是kmp_routine函数地址
- esi设置为2,可能表示有2个参数
- r15设置到rcx,传入线程号参数
- r8传入栈上第0x20个参数,可能是void* shareds参数
- 清空eax,一些调用约定使用
- 调用
__kmpc_fork_call函数,这是OpenMP的runtime库函数,用来并行执行一个函数kmpcfork multiple parallel call?
- 最后将返回值保存在rdi指定的栈空间上
所以这段代码实现了调用OpenMP runtime并行执行一个函数的操作,准备参数,调用runtime API,获取返回值的一个流程。
利用runtime库的支持函数可以实现汇编级别的OpenMP并行性。
readelf
各section位置以及含义,参考文档
1 | $ readelf -S bfs.inj |
字段含义
- Type 字段,具体含义参考文档1-10
- Link 字段中的值是节头表中节头条目的索引,索引从0开始,表示第一个节头表条目,依此类推。比如5 代表与
[ 5] .dynsym有关
值得注意
One section type, SHT_NOBITS described below, occupies no
space in the file, and its sh_offset member locates the conceptual placement in the
file.
so the number “2d258” remains unchanged.
1 | [25] .data PROGBITS 000000000042e258 0002d258 |
.got
global offset table
.plt
This section holds the procedure linkage table. See ‘‘Special Sections’’ in Part 1 and ‘‘Procedure Linkage Table’’ in Part 2 for more information.
Function symbols (those with type STT_FUNC) in shared object files have special significance. When
another object file references a function from a shared object, the link editor automatically creates a procedure linkage table entry for the referenced symbol.
需要进一步的研究学习
暂无
遇到的问题
暂无
开题缘由、总结、反思、吐槽~~
参考文献
上面回答部分来自ChatGPT-3.5,没有进行正确性的交叉校验。
无
llvm
LLVM项目开始于一种比Java字节码更低层级的IR,因此,初始的首字母缩略词是Low Level Virtual Machine。它的想法是发掘低层优化的机会,采用链接时优化。

插一嘴:链接时优化
- GCC也支持链接时优化,称为LTO(Link Time Optimization),通过把多个编译单元中分别生成的目标文件在链接时进行全局的优化,可以提高程序的执行效率。
- 具体内容:大幅度减少可执行文件的体积
- 冗余代码和变量/函数的消除:对于在多个模块中出现的相同代码/变量/函数,链接时优化可以将它们合并,从而减少可执行文件的体积,提高程序的执行效率。
- 内联函数:将函数调用直接替换为函数本身的代码,从而减少函数调用的开销,提高程序的执行效率。
- 循环展开和向量化:内联函数后,或许能进一步将循环展开和向量化,从而减少循环体内的分支判断,优化程序的执行效率。
IR:gcc与llvm的区别
学过编译原理的人都知道,编译过程主要可以划分为前端与后端:
- 前端把源代码翻译成中间表示 (IR)。
- 后端把IR编译成目标平台的机器码。当然,IR也可以给解释器解释执行。
经典的编译器如gcc:在设计上前端到后端编写是强耦合的,你不需要知道,无法知道,也没有API来操作它的IR。
好处是:因为不需要暴露中间过程的接口,编译器可以在内部做任何想做的平台相关的优化。
坏处是,每当一个新的平台出现,这些编译器都要各自为政实现一个从自己的IR到新平台的后端。
- 甚至如果当一种新语言出现,且需要实现一个新的编译器,那么可能需要设计一个新的IR,以及针对大部分平台实现这个IR的后端。
- 如果有M种语言、N种目标平台,那么最坏情况下要实现 M*N 个前后端。这是很低效的。
LLVM的核心设计了一个叫 LLVM IR 的通用中间表示, 并以库(Library) 的方式提供一系列接口, 为你提供诸如操作IR、生成目标平台代码等等后端的功能。
在使用通用IR的情况下,如果有M种语言、N种目标平台,那么最优情况下我们只要实现 M+N 个前后端。
llvm IR
- LLVM IR 中间表示是适用于多种编程语言的通用中间表示,支持C、C++、Objective-C、Swift、Java、Python等多种编程语言。
- 它是一种低级别的语言,类似于汇编语言,但比汇编语言更高级,包含了类型、变量、函数、控制流等高级语言的特性。
- LLVM编译器可以将多种编程语言编译成LLVM IR,从而可以在LLVM IR层面进行各种优化处理,再将LLVM IR转换为目标平台的机器码。
- 比如要将Python脚本编译成LLVM IR中间表示,可以使用Python LLVM编译器llvmlite和numba。
LLVM IR表示与转换
LVM IR实际上有三种表示:
- .ll 格式:人类可以阅读的文本。
- .bc 格式:适合机器存储的二进制文件。
- 内存表示
各种格式是如何生成并相互转换:
| 格式 | 转换命令 |
|---|---|
| .c -> .ll | clang -emit-llvm -S a.c -o a.ll |
| .c -> .bc | clang -emit-llvm -c a.c -o a.bc |
| .ll -> .bc | llvm-as a.ll -o a.bc |
| .bc -> .ll | llvm-dis a.bc -o a.ll |
| .bc -> .s | llc a.bc -o a.s |
对于LLVM IR来说,.ll文件就相当于汇编,.bc文件就相当于机器码。 这也是llvm-as和llvm-dis指令为什么叫as和dis的缘故。
llvm 前端

clang实现的前端包括
- 词法分析(识别标记)
- 处理源代码的文本输入,将语言结构分解为一组单词和标记,去除注释、空白、制表符等。每个单词或者标记必须属于语言子集,语言的保留字被变换为编译器内部表示。
- 词法分析报错的例子包括:拼写错误、注释没有正确结束、字符串没有正确结束等。
- 语法分析(标记结构完整)
- 语法分析器会根据语法规则验证程序的正确性,如缺少右括号、是否缺少关键字、变量未定义、函数应该有返回值等。
- 语义分析(有无语义矛盾)
- 借助符号表检验代码没有违背语言类型系统。这个表存储标识符(符号)和它们各自的类型之间的映射,以及其它内容。
- 类型检查的一种直觉的方法是,在解析之后,遍历AST的同时从符号表收集关于类型的信息。
- 例子:定义了两个变量 a 冲突。
llvm 后端
见 llvm Backend 一文
clang
clang 与 llvm的关系
Clang 是 LLVM 项目中的一个 C/C++/Objective-C 编译器,它使用 LLVM 的前端和后端进行代码生成和优化。它可以将 C/C++/Objective-C 代码编译为 LLVM 的中间表示(LLVM IR),然后进一步将其转换为目标平台的机器码。Clang 拥有很好的错误信息展示和提示,支持多平台使用,是许多开发者的首选编译器之一。同时,Clang 也作为 LLVM 项目的一个前端,为 LLVM 的生态系统提供了广泛的支持和应用。
clang 的开发与苹果公司的关系
Clang 的开发起源于苹果公司的一个项目,即 LLVM/Clang 项目。在 2005 年,苹果公司希望能够使用一种更加灵活、可扩展、优化的编译器来替代 GCC 作为其操作系统 macOS (Mac OS X) 开发环境的默认编译器。由于当时的 GCC 开发被其维护者们认为变得缓慢和难以维护,苹果公司决定开发一款新的编译器,这就是 Clang 诞生的原因。Clang 的开发团队由该项目的创立者 Chris Lattner 领导,他带领团队将 Clang 发展为一款可扩展、模块化、高效的编译器,并成功地将其嵌入到苹果公司的开发工具链 Xcode 中,成为了 macOS 开发环境中默认的编译器之一。
Clang 是一个开源项目,在苹果公司的支持下,Clang 的开发得到了全球各地的开发者们的广泛参与和贡献。现在,Clang 成为了 LLVM 生态中的一个重要组成部分,被广泛地应用于多平台的编译器开发中。
clang-cannot-find-iostream
Clang and Clang++ “borrow” the header files from GCC & G++. It looks for the directories these usually live in and picks the latest one. If you’ve installed a later GCC without the corresponding G++, Clang++ gets confused and can’t find header files. In your instance, for example, if you’ve installed gcc 11 or 12.
You can use clang-10 -v -E or clang++-10 -v -E to get details on what versions of header files it’s trying to use.
安装g++-12解决
常用工具
github/tools目录下有许多实用工具
llvm-as:把LLVM IR从人类能看懂的文本格式汇编成二进制格式。注意:此处得到的不是目标平台的机器码。llvm-dis:llvm-as的逆过程,即反汇编。 不过这里的反汇编的对象是LLVM IR的二进制格式,而不是机器码。opt:优化LLVM IR。输出新的LLVM IR。llc:把LLVM IR编译成汇编码。需要用as进一步得到机器码。lli:解释执行LLVM IR。
需要进一步的研究学习
暂无
遇到的问题
暂无
开题缘由、总结、反思、吐槽~~
参考文献
文章部分内容来自ChatGPT-3.5,暂时没有校验其可靠性(看上去貌似说得通)。
关于X86 与 arm的寄存器的区别写在了arm那篇下
IDA analysis

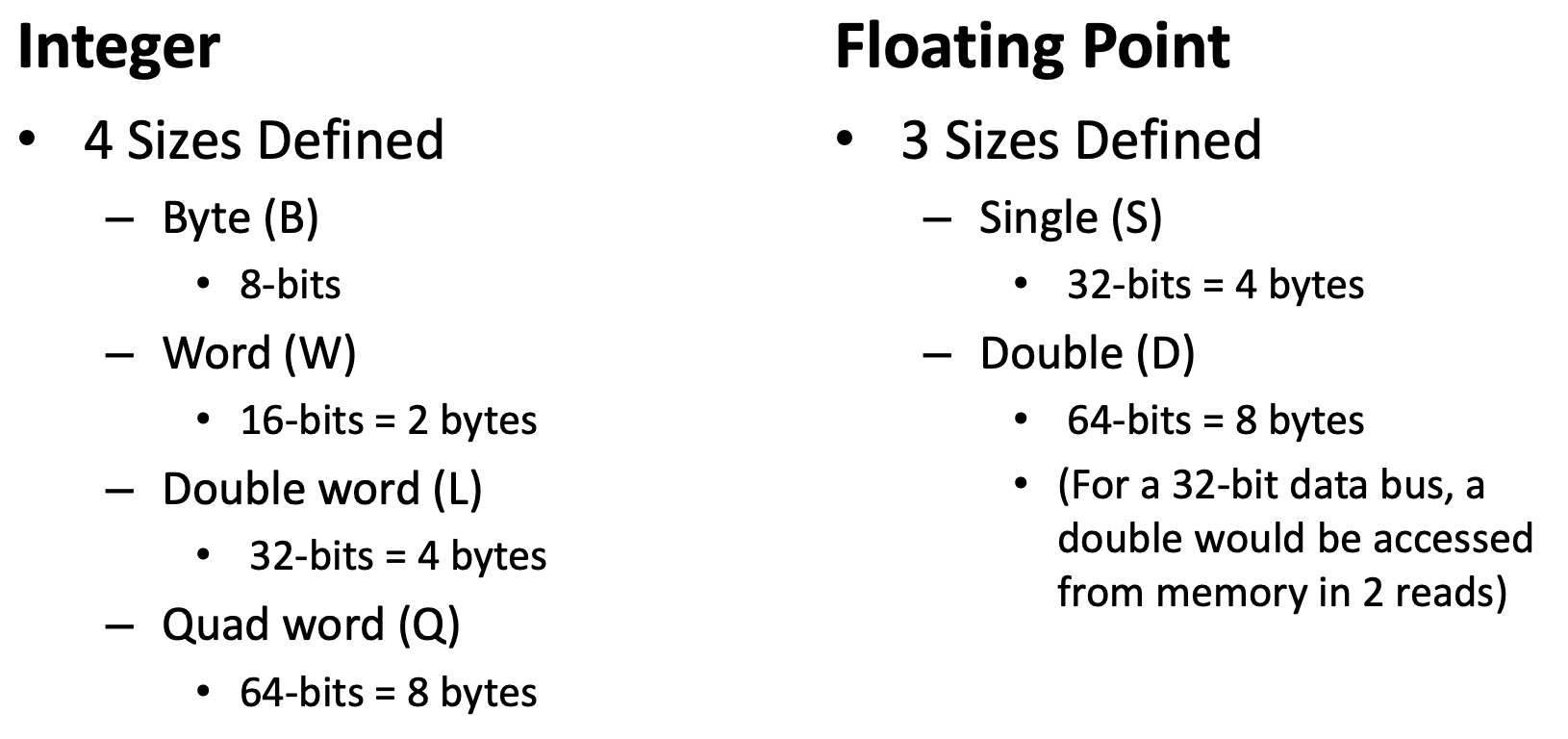
word/ dword/ qword
In x86 terminology/documentation, a “word” is 16 bits
x86 word = 2 bytes
x86 dword = 4 bytes (double word)
x86 qword = 8 bytes (quad word)
x86 double-quad or xmmword = 16 bytes, e.g. movdqa xmm0, [rdi].
常见X86汇编
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X86_instruction_listings
https://www.felixcloutier.com/x86/
https://officedaytime.com/simd512e/
1 | SHR # Shift right (unsigned shift right) |
lea & leaq
1 | lea -0xc(%ebp),%eax |
1 | // x is %rdi, result is %rax 就是计算地址,没有寻址操作 |

call & ret
Call 地址:返回地址入栈(等价于“Push %eip,mov 地址,%eip”;注意eip指向下一条尚未执行的指令)ret:从栈中弹出地址,并跳到那个地址(pop %eip)
leave
leave:使栈做好返回准备,等价于
1 | mov %ebp,%esp |
compare order
1 | cmpl $0x5,$0x1 |
X86 load store
X86 不像 ARM有专门的ldr, str指令。是通过mov实现的
movswl (%rdi), %eax sign-extending load from word (w) to dword (l). Intel movsx eax, word [rdi]
AVX
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E36784_01/html/E36859/gntbd.html
1 | vxorpd XORPD |
test & jump
1 | test al, al |
The test instruction performs a logical and of the two operands and sets the CPU flags register according to the result (which is not stored anywhere). If al is zero, the anded result is zero and that sets the Z flag. If al is nonzero, it clears the Z flag. (Other flags, such as Carry, oVerflow, Sign, Parity, etc. are affected too, but this code has no instruction testing them.)
The jne instruction alters EIP if the Z flag is not set. There is another mnemonic for the same operation called jnz.
1 | test %eax,%eax |
注意 cmp不等于 test
The TEST operation sets the flags CF and OF to zero.
The SF is set to the MSB(most significant bit) of the result of the AND.
If the result of the AND is 0, the ZF is set to 1, otherwise set to 0.
kinds of jump

AT&T syntax jmpq *0x402390(,%rax,8) into INTEL-syntax: jmp [RAX*8 + 0x402390].
ja VS jg
JUMP IF ABOVE AND JUMP IF GREATER
ja jumps if CF = 0 and ZF = 0 (unsigned Above: no carry and not equal)
jg jumps if SF = OF and ZF = 0 (signed Greater, excluding equal)
FLAGS
cmp performs a sub (but does not keep the result).
cmp eax, ebx
Let’s do the same by hand:
1 | reg hex value binary value |
The flags are set as follows:
1 | OF (overflow) : did bit 31 change -> no |
Carry Flag
Carry Flag is a flag set when:
a) two unsigned numbers were added and the result is larger than “capacity” of register where it is saved.
Ex: we wanna add two 8 bit numbers and save result in 8 bit register. In your example: 255 + 9 = 264 which is more that 8 bit register can store. So the value “8” will be saved there (264 & 255 = 8) and CF flag will be set.
b) two unsigned numbers were subtracted and we subtracted the bigger one from the smaller one.
Ex: 1-2 will give you 255 in result and CF flag will be set.
Auxiliary Flag is used as CF but when working with BCD. So AF will be set when we have overflow or underflow on in BCD calculations. For example: considering 8 bit ALU unit, Auxiliary flag is set when there is carry from 3rd bit to 4th bit i.e. carry from lower nibble to higher nibble. (Wiki link)
Overflow Flag is used as CF but when we work on signed numbers.
Ex we wanna add two 8 bit signed numbers: 127 + 2. the result is 129 but it is too much for 8bit signed number, so OF will be set.
Similar when the result is too small like -128 - 1 = -129 which is out of scope for 8 bit signed numbers.
register signed & unsigned
Positive or negative
The CPU does not know (or care) whether a number is positive or negative. The only person who knows is you. If you test SF and OF, then you treat the number as signed. If you only test CF then you treat the number as unsigned.
In order to help you the processor keeps track of all flags at once. You decide which flags to test and by doing so, you decide how to interpret the numbers.
register multiply
The computer makes use of binary multiplication(AND), followed by bit shift (in the direction in which the multiplication proceeds), followed by binary addition(OR).
1 | 1100100 |
for more:
How computer multiplies 2 numbers?
And:
Binary multiplier - Wikipedia
Memory and Addressing Modes
声明静态代码区域
DB, DW, and DD can be used to declare one, two, and four byte data locations,
1 | # 基本例子 |
数组的声明,The DUP directive tells the assembler to duplicate an expression a given number of times. For example, 4 DUP(2) is equivalent to 2, 2, 2, 2.
1 |
|
寻址
32位X86机器寻址支持
- 最多支持32位寄存器和32位有符号常数相加
- 其中一个寄存器可以再乘上 2,4,8
1 | # right |
指定存储在地址的数据大小
1 | mov BYTE PTR [ebx], 2 ; Move 2 into the single byte at the address stored in EBX. |
汇编寄存器顺序,作用方向
这和汇编器语法有关:
X86 instructions
For instructions with two operands, the first (lefthand) operand is the source operand, and the second (righthand) operand is the destination operand (that is, source->destination).
1 | mov eax, ebx — copy the value in ebx into eax |
AT&T syntax
AT&T Syntax is an assembly syntax used in UNIX environments, that originates from AT&T Bell Labs. It is descended from the MIPS assembly syntax. (AT&T, American Telephone & Telegraph)
AT&T Syntax is an assembly syntax used mostly in UNIX environments or by tools like gcc that originated in that environment.

语法特点:https://stackoverflow.com/tags/att/info
需要注意的:
- Operands are in destination-last order
- Register names are prefixed with
%, and immediates are prefixed with$sub $24, %rspreserves 24 bytes on the stack.
- Operand-size is indicated with a
b/w/l/qsuffix on the mnemonicaddb $1, byte_table(%rdi)increment a byte in a static table.- The mov suffix (b, w, l, or q) indicates how many bytes are being copied (1, 2, 4, or 8 respectively)
imul $13, 16(%rdi, %rcx, 4), %eax32-bit load fromrdi + rcx<<2 + 16, multiply that by 13, put the result in%eax. Intelimul eax, [16 + rdi + rcx*4], 13.movswl (%rdi), %eaxsign-extending load from word (w) to dword (l). Intelmovsx eax, word [rdi].
Intel syntax (used in Intel/AMD manuals).
The Intel assembler(icc,icpc我猜) uses the opposite order (destination<-source) for operands.
语法特点: https://stackoverflow.com/tags/intel-syntax/info
RISC-V
1 | beq rs1, rs2, Label #RISC-V |
反汇编器
但是这个语法不是很重要,因为decompiler有选项控制语法
objdump has -Mintel flag, gdb has set disassembly-flavor intel option.
gcc -masm=intel -S or objdump -drwC -Mintel.
需要进一步的研究学习
暂无
遇到的问题
暂无